Top 10 Bitcoin Misconceptions Explained
Bitcoin has garnered significant attention since its inception. However, amidst its rising popularity, numerous misconceptions have emerged, clouding the true nature and potential of this groundbreaking digital currency. We aim to dispel these misconceptions and shed light on the realities of Bitcoin. By unravelling the truth, we hope to provide a comprehensive understanding of Bitcoin’s capabilities, limitations, and place in Africa’s evolving financial landscape.
#1 Bitcoin is Anonymous: Unveiling the Pseudonymous Nature
One prevailing myth surrounding Bitcoin is its supposed anonymity. Contrary to popular belief, Bitcoin is not entirely anonymous, but rather pseudonymous. Each Bitcoin transaction is recorded on the blockchain, a public ledger accessible to all. While users’ real identities remain hidden, the transparency of the blockchain allows for traceability. Addressing this misconception promotes a better understanding of the importance of privacy-enhancing tools and the need for responsible use.
However, it is important to note that users can enhance their privacy by employing certain techniques. When receiving funds, it’s a good idea to use a new address each time. You can try using Sparrow Wallet as it automatically generates a new address each time you want to receive Bitcoin. You can also use privacy tools like mixers and tumblers to make it even more difficult to trace your transactions and follow the flow of your transactions.
We also recommend enhancing your privacy by avoiding the Know Your Customer (KYC) process. Frankly, it is nobody’s business if you are buying or selling Bitcoin. Using Peer to Peer exchanges such as those recommended on our site will help you avoid this and protect your personal information.
Understanding the pseudonymous nature of Bitcoin encourages users to explore privacy-enhancing measures and promotes the responsible use of Bitcoin.
#2 Bitcoin is Used Exclusively for Illicit Activities: Debunking the Myth
No currency is more used for illegal activities than the US Dollar so this is a spurious allegation at best. This reputation of Bitcoin’s association with illicit activities is owing to its early adoption by certain underground markets. However, it is essential to recognize that Bitcoin’s potential extends far beyond illicit transactions. When Bitcoin first emerged, its pseudonymous nature caught the attention of some individuals seeking to engage in unlawful activities. But let’s set the record straight. Bitcoin’s transparency and traceability have proven to be powerful deterrents for those with nefarious intentions.
Bitcoin operates on a decentralized public ledger called a Blockchain. Every transaction is recorded publicly and verified by multiple participants, making it one of the most transparent and traceable financial systems ever created. This transparency is a fundamental feature of Bitcoin that sets it apart from traditional banking systems. While the identities of the participants are not always directly linked to their wallet addresses, the transactions themselves are transparent and can be traced.
It is also important to note that fiat currencies are also used for illegal purposes. The misuse of any form of currency does not represent the entire system or its legitimate uses. Bitcoin has gained significant adoption as a legitimate financial instrument. Its transparency and immutability suit various legitimate use cases, such as remittances, cross-border transactions, and charitable donations. It is essential to separate the technology itself from its association with illicit activities to fully appreciate its potential benefits.
#3 Bitcoin is a Bubble Waiting to Burst: Separating Fact from Fiction
Amidst Bitcoin’s surges in value, skeptics often claim that it is a speculative bubble destined to burst. While Bitcoin has experienced volatile price fluctuations, attributing them solely to a speculative bubble overlooks the underlying technology and its increasing adoption by reputable institutions. Recognizing Bitcoin’s potential as a store of value and a medium of exchange contributes to a more accurate assessment of its long-term prospects.
While it is true that Bitcoin has experienced significant price volatility, it is important to understand the factors contributing to this volatility, such as market sentiment, regulatory developments, and macroeconomic conditions. Additionally, attributing Bitcoin’s value solely to speculation disregards its emergence as a store of value and a medium of exchange.
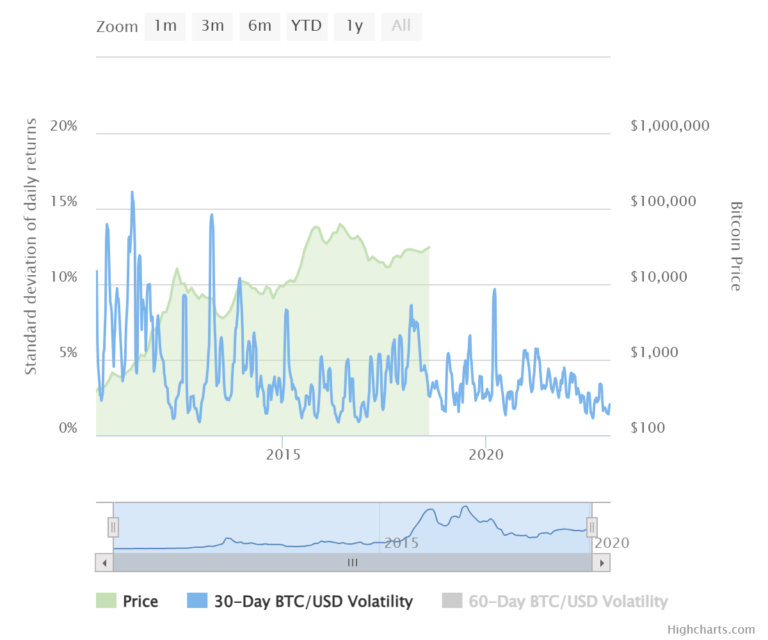
These statistics suggest that Bitcoin’s volatility has been steadily decreasing since its invention in 2009, with a considerable decline since 2022, which is a positive trend for Bitcoiners and the overall perception of Bitcoin as a viable savings option. And as Bitcoin becomes more widely adopted and recognized as a store of value, its volatility is expected to decrease.
Many Bitcoiners are treating Bitcoin as a long-term savings option, because no one has ever lost money by saving a fixed amount of Bitcoin monthly over the space of 5 years. In recent years, reputable institutions, including major financial firms and corporations like Micro Strategy, Square, and even stores like PicknPay, have begun embracing Bitcoin and integrating it into their operations. This institutional adoption lends credibility to Bitcoin and signals its potential long-term viability. The maturing of the Bitcoin market, with increased participation from institutions and mainstream investors, has contributed to the decrease in volatility.
Recognizing Bitcoin’s potential beyond speculation is crucial to accurately assessing its role in the future of finance.
#4 Bitcoin is Controlled by a Single Entity: Understanding Decentralization
Bitcoin’s decentralized nature is often misunderstood, with some believing that it is controlled by a central authority. In reality, Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network called a blockchain. This blockchain is a distributed ledger maintained by a network of nodes and miners. These nodes verify the ledger and the miners play a vital role in validating transactions, securing the network, and reaching a consensus on the state of the blockchain. It’s essential to note that no single entity or organization has complete control over Bitcoin.
Now, let’s address the concern that the code of Bitcoin can be altered. While it’s true that the Bitcoin code can be updated, any proposed changes must go through a rigorous consensus process. This process involves active participation and agreement from a large network of miners, developers, and users. Therefore, altering the code in a way that undermines the decentralization and integrity of Bitcoin is highly unlikely and goes against the core principles of the community.
#5 Bitcoin is Too Complex for Mainstream Adoption: Simplifying the User Experience
Bitcoin’s underlying technology, such as cryptographic keys and blockchain, can be intimidating for newcomers, but the reality is that they shouldn’t need to understand any of this. Over the years, significant progress has been made in enhancing the user experience and simplifying the onboarding process.
User-friendly Bitcoin wallets and intuitive platforms have been developed to streamline the experience of buying, storing, and transacting with Bitcoin. Wallets like Machankura can also be used to make Bitcoin transactions without internet connections. These wallets provide a familiar and easy-to-use interface, making them more accessible for individuals with limited technical expertise.
Furthermore, various educational resources, tutorials, and communities have emerged to help users understand the intricacies of Bitcoin and navigate its landscape. By prioritising education and user-friendly interfaces like Pheonix Wallet and Sparrow Wallet, Bitcoin is gradually becoming more accessible to mainstream users, paving the way for broader adoption and integration into everyday life.
#6 Bitcoin is Prone to Hacks and Security Breaches: Emphasizing that the Bitcoin protocol is hack-proof to date
Bitcoin has never been hacked despite if offering the most lucrative target for hackers that has ever existed. It is important to distinguish between hacks and security breaches that occur within Bitcoin-related services, such as exchanges and wallets, and the actual Bitcoin network itself. While Bitcoin-related services have experienced security incidents in the past, the Bitcoin network has never been hacked or compromised since its inception in 2009. Its decentralized nature, combined with the robustness of the underlying cryptography, has proven resilient against hacking attempts, providing users with a secure and transparent transaction system.
The Bitcoin community and developers continue to work on enhancing the security of Bitcoin-related services and implementing robust security measures. Many reputable wallet providers have implemented strong security protocols, such as two-factor authentication, Brain wallets, cold storage solutions, and multi-signature wallets, to safeguard users’ funds and information.
To safeguard your Bitcoin holdings, we advise users to adopt best security practices. This includes using noncustodial wallets, which allow you to hold your private keys and provide an added layer of protection against cyber threats. Additionally, practicing good digital hygiene, such as using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and keeping software up to date, can significantly mitigate the risk of security breaches.
#7 Bitcoin is Environmentally Unfriendly: Recognizing the Pursuit of Sustainable Solutions
Bitcoin has been criticized for its environmental impact due to its energy-intensive mining process. This is unfair not only because it assumes that the value of the Bitcoin network doesn’t justify the energy usage (it does), it also fails to recognize the type of energy Bitcoin mining uses. Mining only really makes economic sense when the energy is free or close to it. This increasingly means using only stranded or unutilized energy that can’t be sold to the market.
According to a World Economic Forum article, up to 78% of the energy used in Bitcoin mining is already derived from renewable sources. This transition to renewables helps reduce the carbon footprint associated with Bitcoin mining and contributes to a greener energy mix.
Typically, power grids are designed for peak demand, not average daily usage. This means they must be capable of handling high electricity demands during extreme situations, like when everyone has all their electric appliances on at once. This means that oftentimes, power grids have more electricity supply than demand So the rest of the unutilized power can easily be wasted. Bitcoin miners buy this surplus power and use it on their fully mobile mining containers during regular periods when demand is lower. When demand surges, These miners can scale back or temporarily halt operations. So instead of letting the excess power go to waste, it is also monetized through Bitcoin mining making the electricity generation more economical.
There are already Bitcoin mining operations in existence that utilize stranded and unutilized energy to mine Bitcoin. Like how Great American Mining monetizes waste gases from environmentally hazardous activities like gas flaring in the oil and gas industries to power Bitcoin mining machines. Gridless powering rural areas in Kenya and South Sudan through Bitcoin mining with excess hydropower. These are cases of how Bitcoin miners are salvaging stranded energy by setting up mining operations near these energy sources, reducing the need for additional energy infrastructure, promoting the efficient use of existing resources, and contributing to the development of renewable energy projects in remote areas.
Furthermore, Bitcoin mining can help remote communities build out their power generation infrastructure. In areas where traditional electricity access is limited or nonexistent, renewable mini-grids can be established to power these communities. Mini-grids are small-scale energy distribution networks that operate independently of the main power grid. They can be powered by renewable energy sources and provide electricity to villages, communities, or even entire islands. Bitcoin mining operations can contribute to the viability and financial sustainability of these mini-grids by acting as an anchor load, ensuring a consistent demand for the generated energy.
It is also important to note that advancements in mining hardware have led to increased energy efficiency. The development of more energy-efficient mining rigs reduces the carbon footprint associated with Bitcoin mining.
#8 Bitcoin has No Real-World Use Cases: Exploring Daily Transaction Volumes
Bitcoin, as a decentralized peer-to-peer payment network, has often been criticized for its perceived lack of real-world use cases. However, this myth fails to acknowledge the growing adoption of Bitcoin in various sectors and the increasing value of transactions settled on the Bitcoin network each month.
Bitcoin has enabled financial inclusion in areas with limited access to banking services, providing individuals with a secure and decentralized means of storing and transferring value. Furthermore, Bitcoin serves as a hedge against inflation and economic uncertainties in countries experiencing unstable monetary systems. Brick-and-mortar establishments such as restaurants, apartments, and law firms have started accepting Bitcoin as a form of payment alongside popular online services. and we have a map highlighting this rapid acceptance of Bitcoin for payment.
The acceptance and use of Bitcoin by these entities demonstrate its practical application in everyday transactions, with Billions of dollars worth of Bitcoin being exchanged daily.
#9 Bitcoin is a Passing Fad and has no future: Recognizing Long-Term Viability
The perception that Bitcoin is a passing fad fails to acknowledge the significant impact it has already had on the financial landscape. Bitcoin was created in 2009, which means it has been in existence for over 14 years. Its longevity and continued relevance in the ever-evolving cryptocurrency market, despite the perception right from inception that the digital currency has no future, is a testament to its durability and potential for the future. And as more institutions and individuals recognize its potential, Bitcoin’s long-term viability becomes evident.
Despite the fact that Bitcoin has been in circulation for just over a decade, many are ditching the obviously flawed traditional banking system for “New money”. Bitcoin’s decentralized nature eliminates the need for central authorities and empowers individuals to have direct control over their funds. Its transactions typically involve lower fees for cross-border payments compared to traditional financial systems, making it an attractive option for international trade and remittances. The absence of intermediaries and cryptographic algorithms contributes to cost savings, making it attractive for businesses.
Bitcoin’s decentralized nature and limited supply make it anti-fragile and valuable. The Bitcoin network is distributed globally among many thousands of nodes and millions of users, making it extremely difficult to destroy. Additionally, there will only ever be 21 million bitcoins created, creating scarcity and contributing to its value.
Bitcoin’s open-source protocol allows anyone to see and contribute to its development, ensuring that its evolution is driven by the Bitcoin community. This community is defined as anyone who holds Bitcoin or has an interest in its future, making Bitcoin “the people’s money.”
It’s just a matter of time before everyone gets fed up with the corrupt and selfish government-controlled fiat and embraces the new money.
#10 Bitcoin as a Ponzi Scheme
Critics often compare Bitcoin to a Ponzi scheme, which is an investment fraud that relies on new investors’ funds to pay existing investors. They argue that because Bitcoin’s value is sustained by new participants entering the network, it resembles a Ponzi scheme. However, this claim does not hold true when examined closely.
Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network, meaning it is not controlled by any central authority. Its value is determined by a combination of factors such as utility, scarcity, and market demand. Unlike a Ponzi scheme, Bitcoin does not promise guaranteed returns or depend on a continuous influx of new investors. Its value is determined by market dynamics and influenced by factors like adoption, technological advancements, and macroeconomic conditions.
In essence, Bitcoin’s value is driven by market forces and not by a fraudulent scheme.
Get our weekly African Bitcoin updates
"*" indicates required fields
